It can be a bewildering subject. How do I charge my electric vehicle? What will it cost to charge? What type of charger should I use? Many of these questions and more come to mind. But fear not, we've made this handy guide that should answer all of your questions regarding electric vehicle charging! You can find everything you need to know about electric vehicle charging in this handy guide!
Electric Vehicle charging sometimes feels like you need to be an electrical engineer to understand it. However, it’s not that difficult! Using your electric vehicle charging cable, you simply plug your vehicle into the mains electricity (this can be a 3-pin plug or into a dedicated charge point). Electric vehicles generally have charging ports in the same place you would fill up your fuel in a standard vehicle. At the rear of the vehicle (on the left or right). Sometimes though, for example the Nissan Leaf, this charging inlet is under the bonnet.
There are three different types of electric vehicle charge points, slow, fast and rapid. All electric vehicles can use these charge points to fuel up.

Up to 3.7kw, usually only found in home charge points. Ideal for a cost-effective way to charge up your vehicle overnight.

7kw-22kw charge points. 7kw chargers are a common home charge point and charge a vehicle over twice as fast as a 3.7kw charger. Generally, 22kW chargers are not found in homes and are solely available in public charging bays.

These chargers are the real bee's knees and can only be found at dedicated public charging bays. Many rapid chargers offer both AC (up to 43kw) and DC (up to 50kw) charging options
Note: Chargers above 11kW require a 3-phase electrical supply. This is generally only found at commercial properties - even then, not all commercial properties will have a 3-phase supply.
The time your electric vehicle will take to charge depends mainly on two things. The size of your battery and the charge point you are using. Although, charge time can be affected by other aspects such as current charge level, ambient temperature and age of vehicle.
The larger the battery of your electric vehicle, the longer your battery will take to charge however it means you can travel further on a full charge. Your car will charge quicker if you are using a charge point with a higher kW output.
The range you can expect per hour of charging is...
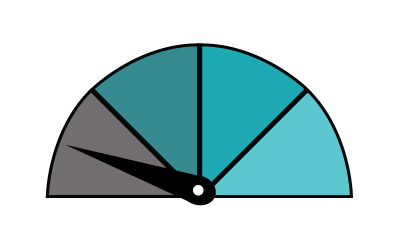
3.7kW - 15 miles
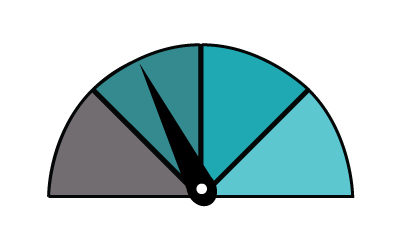
7kW - 30 miles
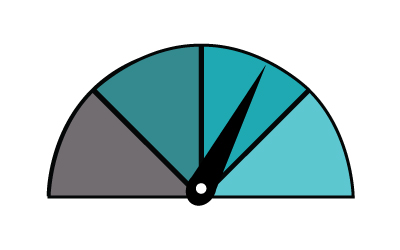
22kW - 80 miles
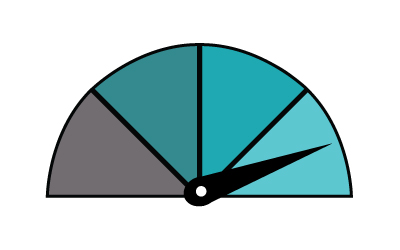
43kW - 155 miles
Not always. This depends on whether you have the correct cable and the type of charger you are at. However, generally, as long as you have the correct cable or cable adapter you will be able to charge at most charge points.
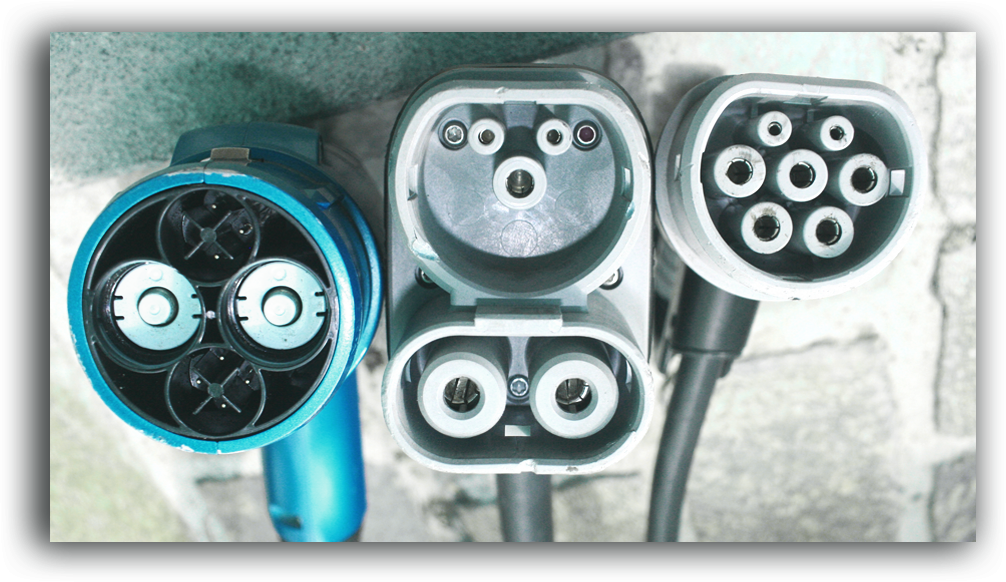
Electric vehicles use a variety of different charging inputs. A lot of EV's have two charging inputs, one for slow/fast charging and another for rapid charging.
Fast public chargers tend to have an un-tethered type 2 output (you have to bring your own cable). In order to find out what output your nearest charger has you can visit ZapMap. This website/app tells you everything you need to know about charging points.
We recommend purchasing a cable with a type 2 (charging point side) which then leads into either a type 1 or 2 (vehicle side) depending on your vehicle. If you really want to be safe, you can purchase a type 2 - type 1 adapter however we don't think this is necessary. As long as you have the correct cable or adapter, you can generally use any fast/slow charger!
 |
Type 1This tends to be the connector of choice for Asian manufacturers. This is the connector that brands such as Mitsubishi and Nissan prefer. |
 |
Type 2European manufacturers prefer this connector mostly. These connectors are used by the likes of Mercedes, VW, Audi and Volvo. |
There are three types of rapid charging inputs:
 |
CHAdeMOVehicles that have a type one inlet for slow/fast charging are paired with a CHAdeMO input also for rapid charging. |
 |
CSSThis input is paired with vehicles that have a type two inlet for slow/fast charging. |
 |
Tesla Type 2This is a rapid charger only found at Tesla Superchargers. Tesla vehicles have a standard type 2 slow/fast charger input as well as their own special rapid charge input. |
No cables need to be purchased for rapid charging. These charge points are not domestic and there will be a tethered (fixed) cable at the rapid charging station.
Standard type 2 chargers can also be used for rapid charging - some vehicles only have a type 2 charger.

You can charge at home out of your standard 3-pin socket with the cable that will be provided with your vehicle.
If you have a home charge point this will either use a type 1, type 2 or in rare cases a commando output (we haven’t discussed these as they are uncommon). You therefore need to purchase the right cable considering this output and your vehicle's slow/fast inlet.
There are two types of cable. 16Amp or 32Amp. We recommend purchasing a 32A cable. As this can still be used with 16A charge points. If you were to use a 16A cable on a 32A charge point you would only be able to access roughly half of the potential power. 32A cables are slightly more expensive, if you only drive to and from your house and do not require public fast charging, a 16A cable may suffice. At many public fast chargers you are charged a connection fee, then charged for the amount of time you are there and/or the kWh you draw. If you are charged based on time at the charger, it is often financially beneficial to buy a 32A cable as this will dramatically speed up your charging time.
Home charging units can only provide a single-phase power output. Public fast and rapid chargers can provide a 3-phase power supply. With 3-phase, more power is transmitted, in a safer manner. If you plan to charge regularly outside of the home environment, we would recommend a 3 phase charger. These are slightly more expensive than single-phase chargers but will save you a lot of charging time when using public fast chargers. It can be financially beneficial to purchase a 3-phase cable due to the faster-charging capability - less time at the charger saves you money.
We recommend spending the extra money for your electric vehicle charging cable. For us, this means purchasing a 32A 3-phase cable with the correct connector for your electric vehicle. This way you will never be caught out without the best cable for charging your vehicle. Please make sure you check what cable comes with your vehicle. Many manufacturers offer free charging cables as standard.
This depends on whether you are using a home charge point or a public one. The cost of home charging depends on the rate set by your electricity company.

Cost of Home Charging |
|
|
UK electricity is charged per kWh of usage. 1 kWh is the equivalent of using an electrical device which uses 1 kW energy output, for one hour. The energy usage you will use at home depends on the power output of your charge point. This will be 2.3kW (a mains plug), 3.7kW (a charge point) or 7kW (an upgraded charge point). By our calculations it would cost approximately £7 to fully charge a Nissan Leaf with a 235 mile range – pretty good value for money! |
|

Cost of Public Charging |
|
|
The cost of public charging varies greatly. Some are free, some charge using their own app and some charge via a contactless payment method. Some operators charge a connection fee. Many charge by the kW (up to 40p) and some charge based on time. Ultimately, public charging can be anywhere between 1.5-3 times the cost of charging a vehicle at home. You can charge a lot faster on public chargers due to their higher power output though. |
|

Cost of Workplace Charging |
|
|
This depends on your workplace. Many workplaces offer free charging as a staff incentive. We do for our staff and customers at our Sheffield office! Other workplaces use a time-based tariff, some offer a free usage limit and then a charge after that limit. Speak with your boss and they should be able to let you know - or point you in the direction of someone who does. |
|
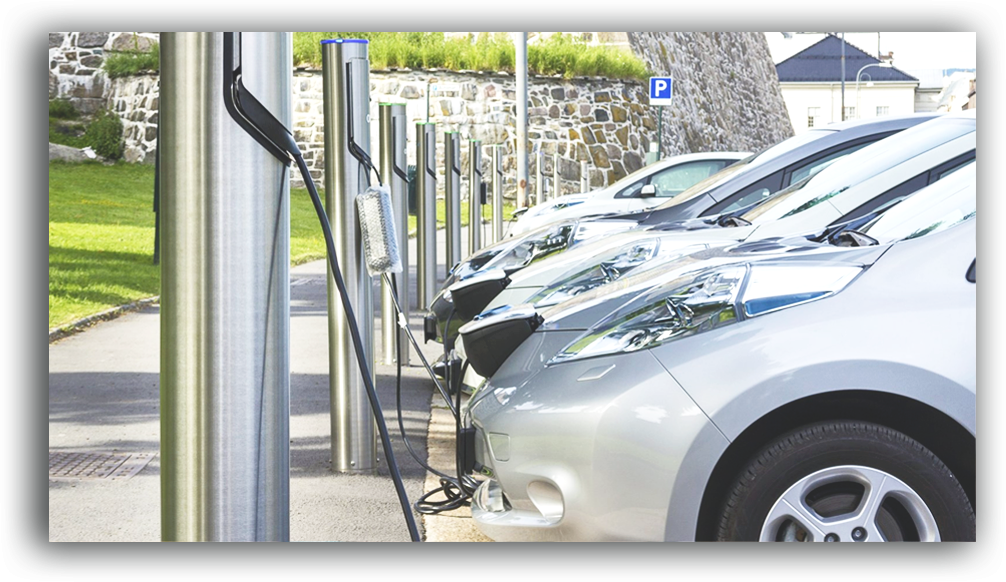

The largest charging network Polar is owned by BP. They have more than 6500 chargers across the UK and charge you £7.85 a month for access. Pod point have teamed up with Tesco to deliver 2400 charge points at over 600 stores in the coming years. Another major player is Ecotricity who have a network of charge points at nearly every motorway service station! We wouldn't recommend any specifically. All of the charging networks have their own benefits. It largely depends on the type of driving you do and the coverage along your driving routes. Many people can manage with home charging alone.
You can install your own charge point at home. Unless you’re handy with electronics, we’d recommend getting a specialist to do this.
There are a few things to consider when doing this…
How fast would you like your vehicle to charge? This depends on your daily life habits. Do you make short trips to home and would like a quick boost to your vehicles range? Or are you a commuter who leaves your vehicle charging overnight? This may affect your decision on the kind of power output you’d like from your charger.

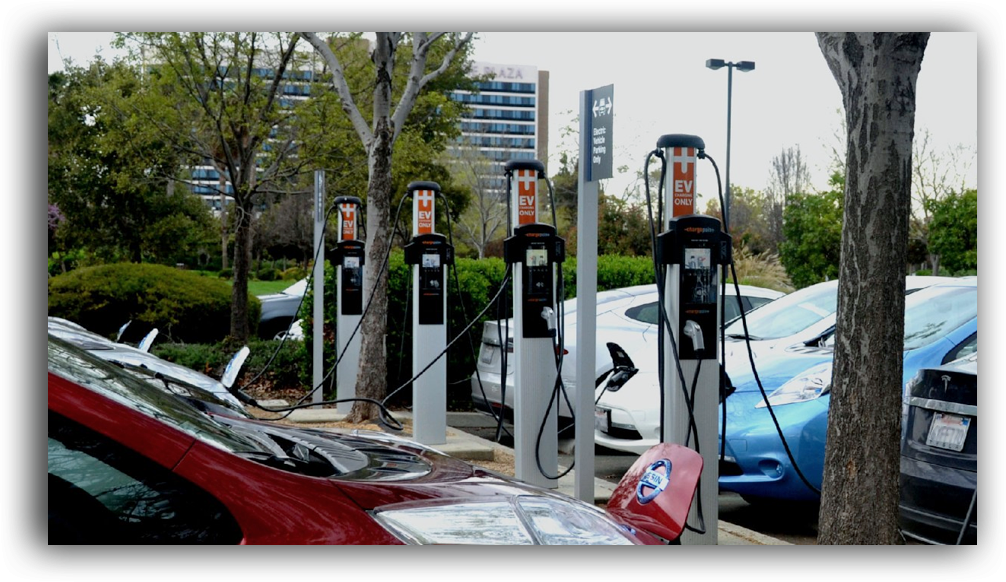
You may need additional electrical work doing on your house depending on where you would like your charge point fitting. If you require multiple charge points or would like a powerful charge point fitting, there may be issues. This depends on the electrical supply of your house.
Do you want a charge point with a built-in cable or a removable one? Having a tethered charge point means you can leave your car or van charging cable in the boot; this ensures you won’t forget it when you leave the house. It’s also quicker to plug in. However, with a tethered cable, you may get caught short when it comes to swapping your vehicle. If your new vehicle has a different connector you may get caught short.

There are several different brands and technologies on the market. Some are more aesthetically pleasing than others this is important for some homeowners. Some charge points are available with different technology such as app integration. These allow you to see how much energy you’ve used in real time and other great features.

We recommend using Go Electric for all your electric vehicle charging needs. Why? Because they have a reputation for great customer service. They’re also a fully accredited installer and servicer of electric vehicle charging points. This means they can install any model of charge point. Giving you more flexibility to find the right solution that suits you.
OLEV stands for office of low emission vehicles and is a governmental agency. In order to try and improve home charging infrastructure and incentivise electric vehicle take up amongst the general population the OLEV grant is currently being offered to businesses and individuals.
You are probably eligible for the grant if you fit the following criteria:
• You’ve not previously claimed the grant
• You have purchased or leased and electric vehicle after April 2015
• You have off street parking
• You’re vehicle is on the OLEV grant eligibility list
• You have chosen to use an OLEV accredited charge point installer

You can claim up to £350 off the cost of installation of a home charge point. You can claim one grant per vehicle that you have (with a maximum of two).
If you live in Scotland, you can claim an extra £300 from the Scottish energy saving trust.
You don’t need to. You’re charge point installer will ask you a few basic questions and they’ll do the rest.

You are probably eligible for a grant if you match the following criteria:
• You are a registered business, charity or public sector organisations and located in the UK.
• You have off-street parking available
• You can demonstrate a clear need for your business to have electric vehicle charging infrastructure
You can claim £350 per charging point and up to 40 charging points.
Your OLEV registered installer will apply for the grant on your behalf.